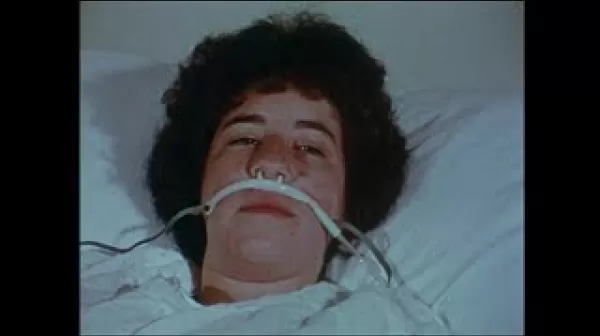
Nurse-Patient Interaction (Los Angeles : The University, 1976)
This training video employs a particular method to encourage nurse trainees to reflect on their responses to how patients and co-workers present themselves, verbally, physically, and emotionally. Based on psychologist Norman Kagan’s affect-stimulus technique, the camera takes the perspective of a trainee nurse who is presented with a series of different people who speak directly to the camera. The viewer is put into the situation of the trainee nurse, and is invited to respond to and reflect upon the different, sometimes difficult, interpersonal situations he or she encounters.