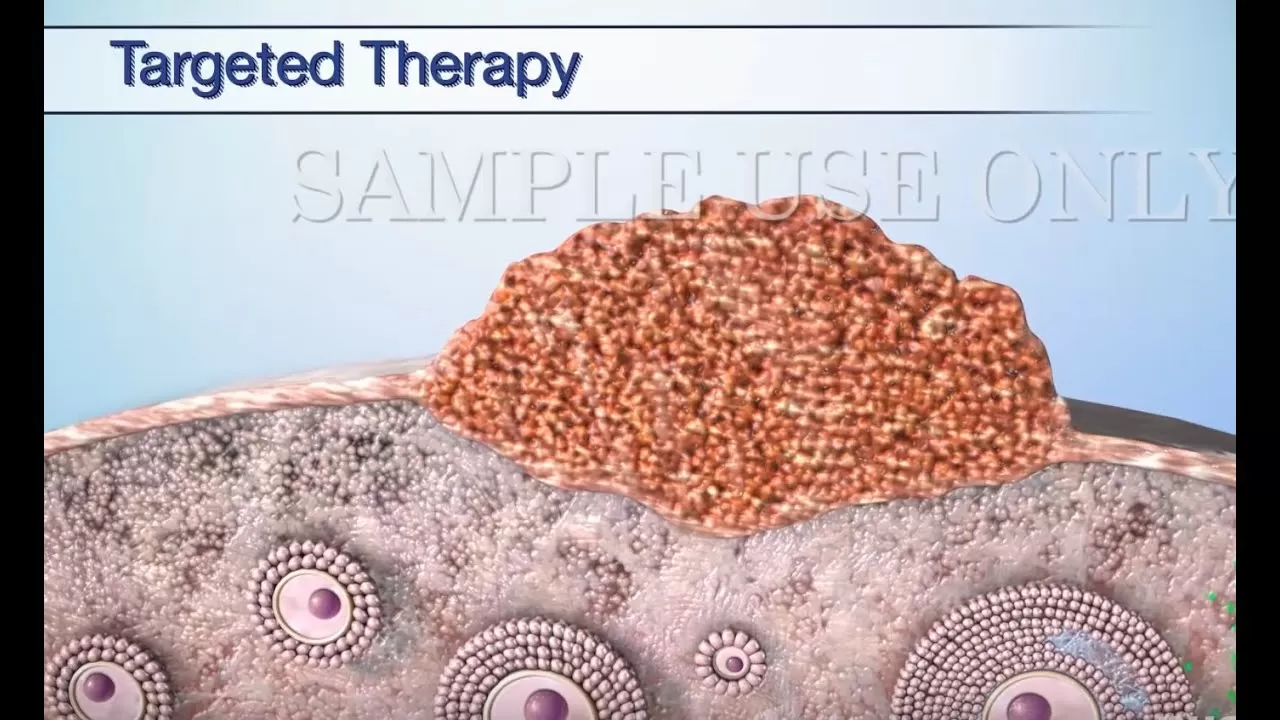
Visit our website to learn more about using Nucleus content for patient engagement and content marketing: http://www.nucleushealth.com/ #OvarianCancerTreatment #OvaryCarcinoma #Ovary MEDICAL ANIMATION TRANSCRIPT: You or someone you care about may have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer. This video will help you understand the treatment options available. Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries which are the part of the reproductive system that makes and stores eggs. Cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow out of control. The cancer cells continue to divide and may spread. Your treatment is based on the type and stage of your cancer and other important factors. The main treatments for ovarian cancer are surgery and chemotherapy. Your treatment plan may include both of these options. You may also receive one or more of the following treatments: targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy. Surgery to remove the tumor is often the first step in your treatment plan. The goal of surgery is to treat your cancer by removing as much of the tumor as possible. If you have epithelial ovarian cancer, the goal is also to stage your cancer. Surgery includes removal of one or both of the ovaries. The affected fallopian tubes may also be removed. If the uterus is removed, surgery may include taking the cervix. To remove as much cancer as possible, the surgeon may need to take tissue from beyond the reproductive system. Lymph nodes or the omentum, which is the apron of tissue that covers your stomach and intestine, may be taken. Surgery may also involve taking tissue from nearby organs, such as the bladder, stomach, or colon. Chemotherapy uses drugs to fight cancer. The drugs enter your bloodstream and travel throughout your body. Chemotherapy works by killing cancer cells or stopping them from dividing. Healthy cells in the body may also be affected, leading to side effects. Targeted therapy is a treatment for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. It targets the part of cancer cells that makes them different from normal cells. These drugs change the way cancer cells divide, grow and repair themselves. As a result, the tumor may stop growing or even shrink. Nearby healthy cells may also be affected, leading to side effects. Immuno-oncology, also known as immunotherapy, helps your immune system fight cancer. These treatments strengthen your immune system so that it can find and attack cancer cells or stop them from growing. Other treatments for ovarian cancer are radiation therapy and hormone therapy. They are used less frequently. Your doctor may prescribe a combination of these treatments. Discuss with your doctor any questions you have about your treatment plan or side effects. Be sure to take your medications as directed by your doctor. ANH15161
Health topics