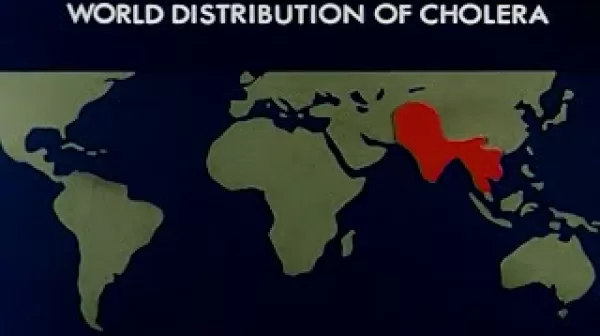
Viral Hepatitis (United States Army, 1952)
This film is a review of viral hepatitis for physicians. The epidemiology, incubation period, immunity, transmission, and incidence of the disease are presented. The symptoms, proper physical examination, laboratory findings, treatment, and pathology of the disease are detailed. The differential diagnosis of viral hepatitis from obstructive jaundice, hemolytic jaundice, infectious mononucleosis, cirrhosis, metastatic carcinoma, toxic hepatitis, Weil's disease, and amebic hepatitis is outlined.