Carcinoma of the Esophagus (Assn of American Medical Colleges, 1953)
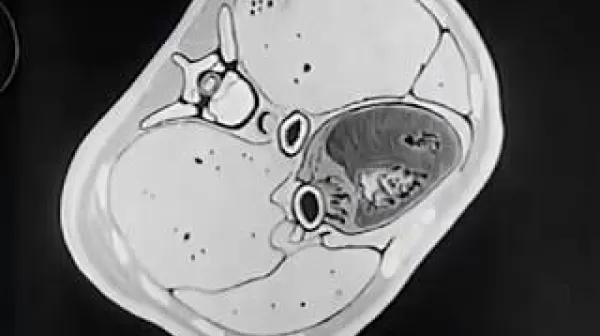
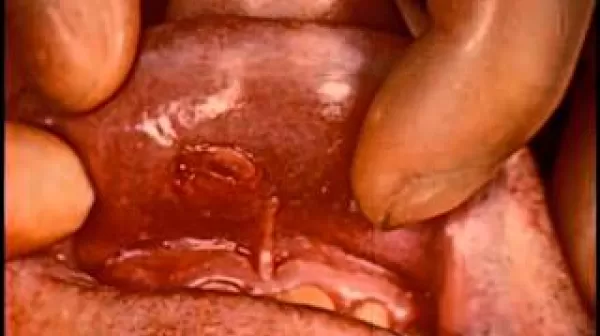
This film shows, by means of cinefluorography and animation, the location of the esophagus and surrounding organs, various irregularities of the esophageal wall created by carcinomas, and the appearance of the area after radiation treatment. Learn more about this film and search its transcript at NLM Digital Collections: http://resource.nlm.nih.gov/8701004A.