Three Counties Against Syphilis (USPHS, 1938)
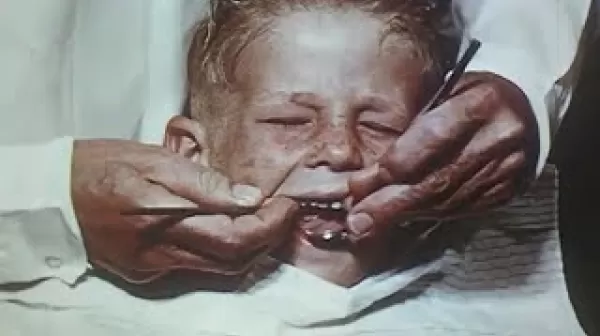
This film shows the work of the mobile syphilis detection and treatment unit of McIntosh, Glynn, and Camden counties in rural southeastern Georgia. The inside of the mobile clinic is shown. The films shows the route taken and the unit going into canneries, wood pulp factories, logging camps, country dance halls, elementary schools, and churches to treat patients with bismuth and arsphenamine injections. It shows both the Kahn and Wasserman blood tests and explains how to read the results.