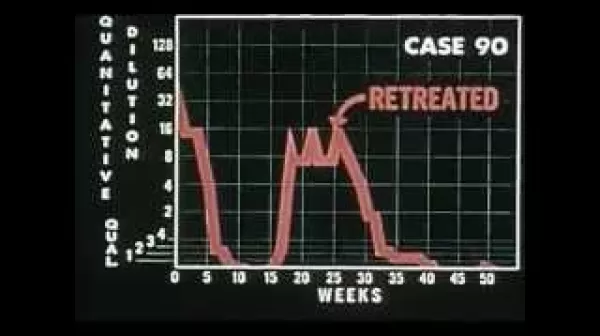
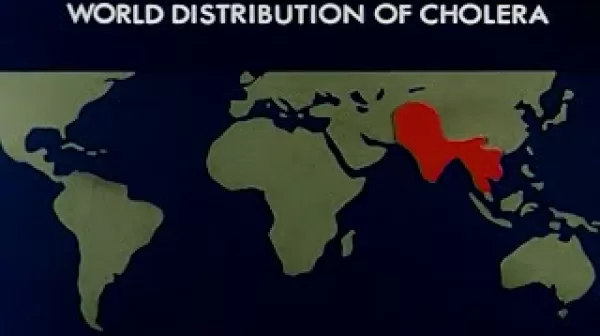
DDT, Weapon Against Disease (US Army, 1945)
The discovery of D.D.T. during World War II, its effectiveness against lice, mosquitoes, and flies; tests made on its effectiveness; and examples of the good results it has shown in controlling military and civilian epidemics are presented. Learn more about this film and search its transcript at NLM Digital Collections: http://resource.nlm.nih.gov/9502511.